
精通
英语
和
开源
,
擅长
开发
与
培训
,
胸怀四海
第一信赖
锐英源精品开源心得,转载请注明出处:锐英源,www.wisestudy.cn,孙老师作品,联系电话13803810136。
下图给出了wireshark功能模块:
处理用户的输入输出显示,源码在gtk目录.
核心模块,通过函数调用将其他模块连接在一起,源码在根目录
wireshark Packetage Analyzing,包分析引擎,源码在epan目录
捕包引擎,利用libpcap/WinPcap从底层抓取网络数据包,libpcap/WinPcap提供了通用的抓包接口,能从不同类型的网络接口(包括以太网,令牌环网,ATM网等)获取数据包。
从文件中读取数据包,支持多种文件格式,源码在wiretap目录
Wireshark抓包时依赖的库文件
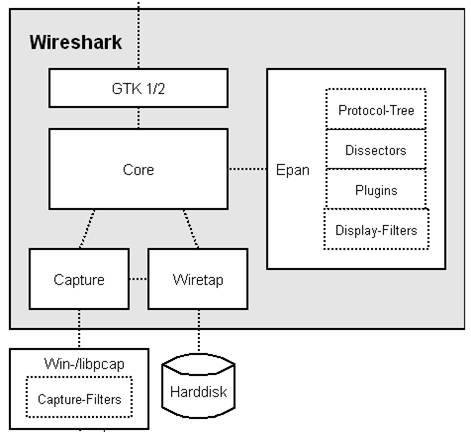
wireshark功能模块
g_log
> since there're lots of log print in the source code of wireshark,I
> want to take a look at the log file after running wireshark.
>
> But I can't find any log files in the installing folder. Can you tell
> me where can I find them Thanks
I assume you're referring to the g_log calls There is a hidden
preference in Wireshark's preferences file (see Help - About - Folders
to see where the Personal Configuration is to find it under the filename
preferences):
######## Console: logging level ########
# (debugging only, not in the Preferences dialog)
# A bitmask of glib log levels:
# G_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR = 4
# G_LOG_LEVEL_CRITICAL = 8
# G_LOG_LEVEL_WARNING = 16
# G_LOG_LEVEL_MESSAGE = 32
# G_LOG_LEVEL_INFO = 64
# G_LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG = 128
console.log.level: 28
This enables the g_log functions to print to the console (not to a log
file). If you're on Windows, make sure to enable the console window in
the Preferences (under the Edit menu). You can see it is set to 28 by
default; that is the sum of the values of G_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, _CRITICAL
and _WARNING.
使用g_printf可以直接输出到控制台窗口上,证明不行,在AlwaysOpen时还是不行
g_warning也是不行,但是用tshark可以看到输出,可能是带窗口的环境,显示有困难吧
http://anonsvn.wireshark.org/wireshark/trunk/doc/README.tapping
The TAP system in Wireshark is a powerful and flexible mechanism to get event
driven notification on packets matching certain protocols and/or filters.
In order to use the tapping system, very little knowledge of Wireshark
internals are required.
As examples on how to use the tap system see the implementation of
tap-rpcstat.c (tshark version)
gtk/rpc_stat.c (gtk-wireshark version)
If all you need is to keep some counters, there's the stats_tree API,
which offers a simple way to make a GUI and tshark tap-listener; see
README.stats_tree. However, keep reading, as you'll need much of what's
in this document.
The tap system consists of two parts:
1, code in the actual dissectors to allow tapping data from that particular
protocol dissector, and
2, event driven code in an extension such as tap-rpcstat.c that registers
a tap listener and processes received data.
So you want to hack together a tap application
主要是统计和通知功能,在epan里的dissector内也有关联代码
入口代码应该是在gtk\main.c下
create_main_window
gtk_main
Wireshark的初始化包括一些全局变量的初始化、协议分析引擎的初始化和Gtk相关初始化,显示Ethereal主窗口,等待用户进一步操作。重点就是Epan模块的初始化。
Epan初始化:
以上三个全局变量主要用来判断新注册的协议名是否重复,如果重复,给出提示信息,在协议解析过程中并没有使用。
Wireshark初始化完成以后进入实际处理阶段,主程序创建抓包进程,捕包进程和主程序是通过PIPE进行传递数据的,主程序把抓取的数据写入临时文件,通过函数add_packet_to_packet_list将数据包加入包列表。处理时,主程序从列表中选取一个数据包,提取该数据包中的数据填写在数据结构中,最后调用协议解析函数epan_dissect_run进行处理,从epan_dissect_run开始,是实际的协议解析过程,
下面以HTTP协议报文为例,流程如下:
调用函数dissect_frame对frame层进行解析,并在协议树上填充相应字段信息。函数最后会判断是否有上层协议封装,如果有则调用函数dissector_try_port在协议树上查找对应的解析函数,这里函数dissector_try_port根据pinfo->fd->lnk_t查找对应的上层协议处理函数,pinfo->fd->lnk_t值为1,上层封装协议为以太网协议,全局结构体指针变量dissector_handle当前的协议解析引擎句柄置为dissect_eth_maybefcs,至此,frame层解析结束。
函数call_dissector_work根据dissector_handle调用frame上层协议解析函数dissect_eth_maybefcs对以太网层进行解析,并在协议树上填充相应字段,包括目的MAC地址和以太网上层协议类型等信息。函数最后会判断是否有上层协议封装,如果有则调用函数dissector_try_port在协议树上查找对应的解析函数,这里函数dissector_try_port根据etype查找对应的上层协议处理函数,以太网字段etype为0800的报文是ip报文,上层封装协议为IP协议,全局结构体指针变量dissector_handle当前的协议解析引擎句柄置为dissect_ip,至此,以太网层解析结束。
函数call_dissector_work根据dissector_handle调用以太网上层协议解析函数dissect_ip对以太网层进行解析,并在协议树上填充相应字段,包括版本号,源地址,目的地址等信息。函数最后会判断是否有上层协议封装,如果有则调用函数dissector_try_port在协议树上查找对应的解析函数,这里函数dissector_try_port根据nxt (nxt = iph->ip_p)查找对应的上层协议处理函数,以太网字段nxt为06的报文是TCP报文,上层封装协议为TCP协议,全局结构体指针变量dissector_handle当前的协议解析引擎句柄置为dissect_tcp,至此,IP层解析结束。
函数call_dissector_work根据dissector_handle调用以太网上层协议解析函数dissect_tcp对TCP层进行解析,包括对TCP头的解析和选项字段的解析,并在协议树上填充相应字段,包括源端口,目的端口,标志位等信息。函数最后会判断是否有上层协议封装,如果有则调用函数dissector_try_port在协议树上查找对应的解析函数,这里函数dissector_try_port根据port查找对应的上层协议处理函数,将源端口和目的端口分别赋值给low_port和high_port,根据low_port和high_port分别匹配上层协议解析函数,port为80的报文是HTTP报文,上层封装协议为HTTP协议,全局结构体指针变量dissector_handle当前的协议解析引擎句柄置为dissect_http,至此,TCP层解析结束。
至此wireshark进入应用层协议检测阶段,wireshark解析dissect_http函数中注册的字段,并提取相应的字段值添加到协议树中,应用层的具体解析流程将在下面介绍。HTTP协议具体函数调用过程参见:
struct _epan_dissect_t {
tvbuff_t *tvb;//用来保存原始数据包
proto_tree *tree;//协议树结构
packet_info pi;// 包括各种关于数据包和协议显示的相关信息
};
/** Each proto_tree, proto_item is one of these. */
typedef struct _proto_node {
struct _proto_node *first_child;//协议树节点的第一个子节点指针
struct _proto_node *last_child; //协议树节点的最后一个子节点指针
struct _proto_node *next; //协议树节点的下一个节点指针
struct _proto_node *parent;//父节点指针
field_info *finfo;//保存当前协议要显示的地段
tree_data_t *tree_data;//协议树信息
} proto_node;
typedef struct _packet_info {
const char *current_proto; //当前正在解析的协议名称
column_info *cinfo; //wireshark显示的信息
frame_data *fd;//现在分析的原始数据指针
union wtap_pseudo_header *pseudo_header;//frame类型信息
GSList *data_src; /*frame层信息 */
address dl_src; /* 源MAC */
address dl_dst; /*目的MAC */
address net_src; /* 源IP */
address net_dst; /*目的IP */
address src; /*源IP */
address dst; /*目的IP */
guint32 ethertype; /*以太网类型字段*/
guint32 ipproto; /* IP协议类型*/
guint32 ipxptype; /* IPX 包类型 */
guint32 mpls_label; /* MPLS包标签*/
circuit_type ctype;
guint32 circuit_id; /*环路ID */
const char *noreassembly_reason; /* 重组失败原因*/
gboolean fragmented; /*为真表示未分片*/
gboolean in_error_pkt; /*错误包标志*/
port_type ptype; /*端口类型 */
guint32 srcport; /*源端口*/
guint32 destport; /*目的端口*/
guint32 match_port; /*进行解析函数匹配时的匹配端口*/
const char *match_string; /*调用子解析引擎时匹配的协议字段指针*/
guint16 can_desegment; /* 能否分段标志*/
guint16 saved_can_desegment;
int desegment_offset; /*分段大小*/
#define DESEGMENT_ONE_MORE_SEGMENT 0x0fffffff
#define DESEGMENT_UNTIL_FIN 0x0ffffffe
guint32 desegment_len;
guint16 want_pdu_tracking;
guint32 bytes_until_next_pdu;
int iplen; /*IP包总长*/
int iphdrlen; /*IP头长度*/
int p2p_dir;
guint16 oxid; /* next 2 fields reqd to identify fibre */
guint16 rxid; /* channel conversations */
guint8 r_ctl; /* R_CTL field in Fibre Channel Protocol */
guint8 sof_eof;
guint16 src_idx; /* Source port index (Cisco MDS-specific) */
guint16 dst_idx; /* Dest port index (Cisco MDS-specific) */
guint16 vsan; /* Fibre channel/Cisco MDS-specific */
/* Extra data for DCERPC handling and tracking of context ids */
guint16 dcectxid; /* Context ID (DCERPC-specific) */
int dcetransporttype;
guint16 dcetransportsalt; /* fid: if transporttype==DCE_CN_TRANSPORT_SMBPIPE */
#define DECRYPT_GSSAPI_NORMAL 1
#define DECRYPT_GSSAPI_DCE 2
guint16 decrypt_gssapi_tvb;
tvbuff_t *gssapi_wrap_tvb;
tvbuff_t *gssapi_encrypted_tvb;
tvbuff_t *gssapi_decrypted_tvb;
gboolean gssapi_data_encrypted;
guint32 ppid; /* SCTP PPI of current DATA chunk */
guint32 ppids[MAX_NUMBER_OF_PPIDS]; /* The first NUMBER_OF_PPIDS PPIDS which are present * in the SCTP packet*/
void *private_data; /* pointer to data passed from one dissector to another */
/* TODO: Use emem_strbuf_t instead */
GString *layer_names; /* layers of each protocol */
guint16 link_number;
guint8 annex_a_used;
guint16 profinet_type; /* the type of PROFINET packet (0: not a PROFINET packet) */
void *profinet_conv; /* the PROFINET conversation data (NULL: not a PROFINET packet) */
void *usb_conv_info;
void *tcp_tree; /* proto_tree for the tcp layer */
const char *dcerpc_procedure_name; /* Used by PIDL to store the name of the current dcerpc procedure */
struct _sccp_msg_info_t* sccp_info;
guint16 clnp_srcref; /* clnp/cotp source reference (can't use srcport, this would confuse tpkt) */
guint16 clnp_dstref; /* clnp/cotp destination reference (can't use dstport, this would confuse tpkt) */
guint16 zbee_cluster_id; /* ZigBee cluster ID, an application-specific message identifier that
* happens to be included in the transport (APS) layer header.
*/
guint8 zbee_stack_vers; int link_dir; /* 3GPP messages are sometime different UP link(UL) or Downlink(DL)*/
} packet_info;
static void
dissect_foo(tvbuff_t *tvb, packet_info *pinfo, proto_tree *tree)
{
col_set_str(pinfo->cinfo, COL_PROTOCOL, "FOO");
/* Clear out stuff in the info column */
col_clear(pinfo->cinfo,COL_INFO);
if (tree) { /* we are being asked for details */
proto_item *ti = NULL;
ti = proto_tree_add_item(tree, proto_foo, tvb, 0, -1, FALSE);
}
}
What we're doing here is adding a subtree to the dissection. This subtree will hold all the details of this protocol and so not clutter up the display when not required.
We are also marking the area of data that is being consumed by this protocol. In our case it's all that has been passed to us, as we're assuming this protocol does not encapsulate another. Therefore, we add the new tree node with proto_tree_add_item(), adding it to the passed in tree, label it with the protocol, use the passed in tvb buffer as the data, and consume from 0 to the end (-1) of this data. The FALSE we'll ignore for now.
对协议中的每个域都会注册一个header_field_info对象,它描述了此协议域的显示名称,filer中的使用的名称,数据类型以及显示格式等等。
TAP的理解
TSHARK_TAP_SRC
踪迹分析程序